Vhdl Code For Serial Adder Using Finite State Machine Equilibrium Unemployment Theory Pissarides Pdf Electric Rain Swift 3d 6.0.933 Python Event Driven Serial Gokusen S2 Sub Indo Consent Form Pm 330 Pdf Cm 03/04 Patch Update Ultramega Ok Zip Download Ennum Ninakkai Padam Mp3. Index Terms — VHDL code, Verilog code, finite state machine, Mealy machine, Moore machine, modeling issues, state encoding. INTRODUCTION The automata theory is the basis behind the traditional model of computation and is used for many purposes other than controller circuit design, including computer program. Vhdl Code For Serial Adder Using Finite State Machine Equilibrium Unemployment Theory Pissarides Pdf Electric Rain Swift 3d 6.0.933 Python Event Driven Serial Gokusen S2 Sub Indo Consent Form Pm 330 Pdf Cm 03/04 Patch Update Ultramega Ok Zip Download Ennum Ninakkai Padam Mp3 Downlod Pusha TExodus Mp3. California State University We study parallel adder circuits: Ripple-carry adder Carry-look ahead adder These adders are fast but expensive If speed is not critical, a more area-efficient scheme is to add the bits a pair at a time; which is called serial adder Serial Adder Using FSM.
- Vhdl Code For Serial Adder Using Finite State Machine Learning
- Vhdl Code For Serial Adder Using Finite State Machine Diagram
- Serial Adder Verilog
- Vhdl Code For Serial Adder Using Finite State Machine Designer
- Vhdl Code For Serial Adder Using Finite State Machine
- Vhdl Code For Serial Adder Using Finite State Machines
Finite state machine is a graphical model/representation of sequential activities or events. After representing and modeling the events they can be implemented easily in case of sequential logic designs. Finite state machines can be utilized in many fields of study e.g neural networks, artificial intelligence, mathematics, games, robotics and sequential flow of data. Since we are dealing with the sequential circuits so i will explain their use in sequential circuit design in this tutorial. |
- Melay Machine
- Moore Machine
Moore Machine
- More number of states in moore compared to melay for same fsm.
- States changes after 1 clock cycle. Latency = 1.
- Synchronous output. Because the states are determined in a process.
- States are output.
Mealy Machine
- Less number of states in mealy compared to moore for same fsm.
- State transition on the same clock cycle. Latency = 0.
- Asynchronous output.
- Transition are output.
VHSIC [Very High Speed Integrated Circuits] Hardware Description Language
IEEE-1076
This is just a quick reference of some short VHDL code fragments. Above each code segment is a circuit which represents the fragment.
In most cases the Process, and end of Process commands are not listed to keep the text down.
VHDL code for a D Flip Flop
process (signal names)
begin
if (clock’event and clock = ‘1’) then
output <= data;
end if;
end process
A 1 bit flip flop is used as the example. but any data width may be used.
Reference; a D Flip Flop Definition and true table.
VHDL code for a D Flip Flop with Reset and Clear
if reset = ‘0’ then
output <= ‘0’;
elsif set = ‘0’ then
output <= ‘1’;
elsif (clock’event and clock = ‘1’) then
output <= data;
end if;
Vhdl Code For Serial Adder Using Finite State Machine Learning
Note that the code show asynchronous Reset and Clear lines, which is fine for the code segment.
However those lines should be synchronized at some point, or insure that no data is used when those lines are valid.
VHDL code for a D Flip Flop
if (clock’event and clock = ‘0’) then
if (reset = ‘0’ and data = ‘0’) then
output <= ‘0’;
elsif (reset = ‘0’ and data = ‘1’) then
output <= ‘0’;
elsif (reset = ‘1’ and data = ‘0’) then
output <= ‘0’;
elsif (reset = ‘1’ and data = ‘1’) then
output <= ‘1’;
end if;
Another flip flop using a reset, but this time just to zero out the data, as in a gating signal.
Again, the rest signal should have been synchronized with the clock at some point [in another code fragment].
VHDL code for a JK Flip Flop
if (clock’event and clock = ‘1’) then
if (in1 = ‘0’ and in2 = ‘0’) then
output <= output;
elsif (in1 = ‘1’ and in2 = ‘0’) then
output <= ‘1’;
elsif (in1 = ‘0’ and in2 = ‘1’) then
output <= ‘0’;
elsif (in1 = ‘1’ and in2 = ‘1’) then
output <= not(output);
end if;
end if;
Reference; a JK Flip Flop Definition and true table.
VHDL code for a 2-to-1 Mux
if sel = ‘0’ then
output <= data1;
elsif sel = ‘1’ then
output <= data2;
end if;
Reference Standard Logic Multiplexer Circuits.
This circuit may be scaled to any data width, and more complicated select functions can be implemented.
VHDL code for a Serial to Parallel Converter
if clear = ‘0’ then
shift_reg <= “00000000”;
elsif (clock’event and clock = ‘1’) then
shift_reg(7 downto 1) <= (6 downto 0);
shift_reg(0) <= serial;
end if;
A common 8 bit data path is coded as an example.
Reference Common Shift Register Functions.
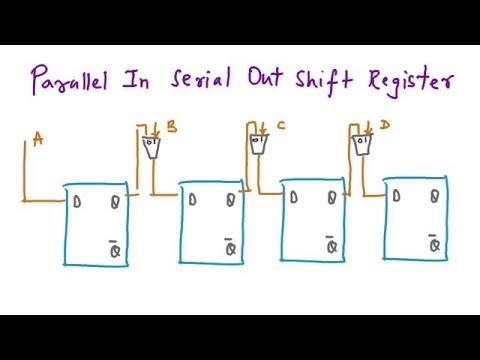
VHDL code for a Parallel to Serial Converter
if load = ‘0’ then
shift_reg <= parallel;
elsif (clock’event and clock = ‘1’) then
serial <= shift_reg(7);
shift_reg(7 downto 1) <= (6 downto 0);
end if;
A common 8 bit data path is coded as an example.
Reference Common Shift Register Functions.
VHDL code for a 4 bit Counter
if load = ‘0’ then
output <= “1111”;
elsif (clock’event and clock = ‘1’) then
output <= data - ‘1’;
end if;
carry <= ‘0’ when output = “0000” else‘1’;
load <= carry;
The code provides a 4 bit down counter function.
Reference common logic functions; Up/Down Decade Counters, or Up/Down Binary Counters.
VHDL code for a 1 bit Adder
if c = ‘0’ then
if (a and b) = ‘1’ then
sum <= ‘0’;
carry <= ‘1’;
elsif (a or b) = ‘1’ then
sum <= ‘1’;
carry <= ‘0’
end if;
elsif c = ‘1’ then
if (a and b) = ‘1’ then
sum <= ‘1’;
carry <= ‘1’;
elsif (a or b) = ‘1’ then
sum <= ‘0’;
carry <= ‘1’;
end if;
end if;
An adder could be a half adder which does not accept a carry in or a full adders that uses a carry input [as shown].
It's assumed that these inputs are some how synchronized with a clock.
Reference; Types of IC Adders, with logic diagram.
VHDL code for a State Machine
if reset = ‘0’ then
state <= stateA;
output <= ‘0’;
elsif (clock’event and clock) = ‘1’ then
case state is
when stateA
output <= ‘0’;
state <= stateB
when stateB
output <= ‘1’;
if input = ‘1’ then
state <= stateB;
else
state <=stateC;
end if;
when stateC
output <= ‘0’
state <= stateA;
end case;
Exclusive-OR Gate
Vhdl Code For Serial Adder Using Finite State Machine Diagram
if (a and b) = ‘1’ then
y <= ‘0’;
elsif (a and b) = ‘0’ then
y <= ‘0’;
else
y <= ‘1’;
end if;
Reference; a Exclusive-OR Gate Definition and true table.
Serial Adder Verilog
IEEE-1076: Standard VHDL Language Reference Manual IEEE Computer Society Document
IEEE 1076.1: VHDL Analog and Mixed-Signal Extensions IEEE Computer Society Document
IEEE 1076.2: Standard VHDL Mathematical Packages IEEE Computer Society Document
IEEE 1076.3: Standard VHDL Synthesis Packages IEEE Computer Society Document
IEEE 1076.4: Standard for VITAL ASIC (Application Specific Integrated Circuit) Modeling Specification IEEE Computer Society Document
IEEE 1076.6: Standard for VHDL Register Transfer Level (RTL) Synthesis IEEE Computer Society Document
Links on this site:
VHDL Sites: Listed here
Back to the Logic Design Page, Digital Logic Pitfalls
VHDL Design Tools: CAD - CAE Products
VHDL Simulation Tools: VHDL Simulation Software Products
FPGA Manufactures: Hardware - Components - Semiconductor- Digital - Programmable Logic
Vhdl Code For Serial Adder Using Finite State Machine Designer
In regards to flip-flops and other examples, there are no constraints on using standard functions.
That is a flip flop does not have to be constrained to a D-type or JK-type function, any number of commands might be used.
The functions provided do relate to an available IC function so comparisons can be made between the firmware and hardware.
Vhdl Code For Serial Adder Using Finite State Machine
| Home | |||||||
| Distributors | Components | Equipment | Software | Standards | Buses | Design | Reference |
Vhdl Code For Serial Adder Using Finite State Machines
© 1998 - 2016 All rights reserved Larry Davis